📖 文档概览
报告标题: 具身智能十大观察核心主题: 洞悉智能发展之势,探索智能向善之路发布时间: 2025年11月核心摘要: 本报告系统性地观察了具身智能(Embodied AI)在技术突破、产业发展、应用场景和治理体系等方面的最新动态。报告指出,在大模型与多模态技术的驱动下,具身智能正成为重要的新经济增长点,但其发展仍面临技术瓶颈、数据治理、伦理安全和人才短缺等挑战,最终目标是实现“智能向善”。
🔍 十大核心观察详解
观察一 核心驱动技术:大模型与多模态融合
大模型技术为具身智能提供了强大的“大脑”,显著提升了语义理解、决策能力和环境适应性。多模态感知与交互技术(视觉、听觉、触觉)的融合,使机器人能更全面地感知环境并进行自然交互。

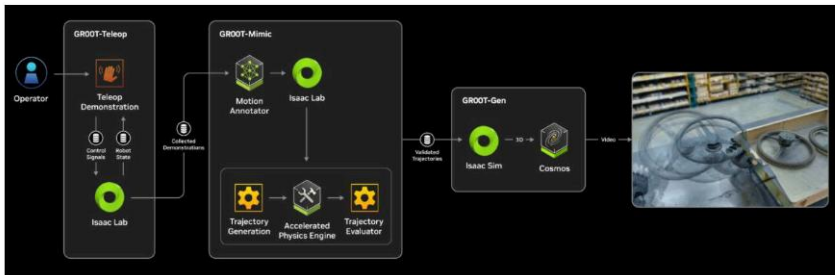
面临挑战: 计算资源需求巨大、数据质量与多样性不足、模型可解释性与安全性、硬件标准化难题。解决方案: 优化算法与硬件、利用合成数据(如NVIDIA Isaac GR00T)、研发可解释性AI、推动硬件标准化。
观察二 产业链瓶颈:关键节点待突破
报告剖析了具身智能的完整产业链。
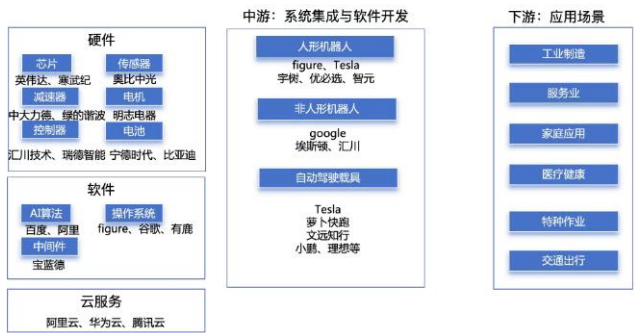
- ∙上游(核心零部件/算法): 高端AI芯片(如英伟达)、传感器、伺服电机等仍存在技术瓶颈,国产替代正在加速。
- ∙中游(系统集成/产品制造): 软硬件集成难度大,“大脑”(认知模型)和“小脑”(运动控制)模型的供应链仍需完善。
- ∙下游(应用场景): 市场需求反馈驱动产业链优化升级。
观察三 应用场景:工业制造为首要突破口
工厂场景因任务明确、环境可控、已有自动化基础,成为人形机器人最先实现规模化落地的突破口。
- ∙工业“实习”潮: 特斯拉Optimus、宝马工厂的Figure 02、优必选Walker S等在汽车工厂执行搬运、装配、质检等任务。
- ∙服务与特种作业: 服务机器人(如1X的EVE)拓展至安保、后勤、养老领域;特种机器人应用于消防、矿山、深海等危险复杂环境。

拓展障碍: 技术能力在复杂环境下不足、成本高昂、市场接受度有待提高。
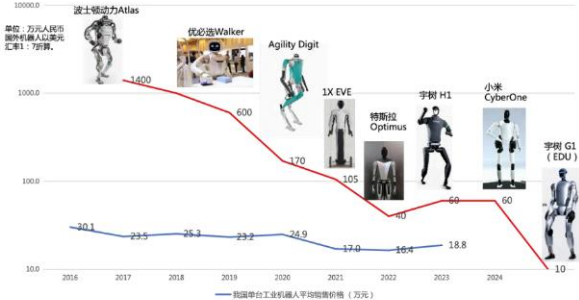
观察四 市场竞争:日益白热化
- ∙市场预测: 全球具身智能系统市场规模预计从2023年的35亿美元增长至2030年的94亿美元(CAGR 15.2%)。
- ∙国际巨头布局:
- ∙英伟达 (NVIDIA): 构建“芯片-平台-模型-仿真”全栈闭环(如Jetson芯片、GR00T模型、Isaac Sim仿真平台)。
- ∙特斯拉 (Tesla): 将其在汽车领域的“规模制造+AI芯片+数据闭环”模式复制到Optimus人形机器人,目标将成本降至1.8万美元以下。
- ∙其他企业: Google(RT系列模型)、OpenAI(投资Figure AI)等纷纷布局。
- ∙国内企业动态: 华为、小米、宇树科技、魔法原子等初创企业及科技巨头在特定领域寻求突破。

观察五至十:发展的基石与方向
| 观察领域 | 核心内容摘要 |
|---|---|
| 观察五:数据治理与隐私保护 | 数据是具身智能的“燃料”。需应对数据收集、标注的挑战,并通过加密技术、访问控制和完善的管理体系保障数据安全与隐私。 |
| 观察六:伦理与安全规范 | 需防范人机交互伦理问题与机器人行为失控风险。国内外正在加快相关标准制定(如欧盟《人工智能法案》),企业需将安全伦理融入设计。 |
| 观察七:智能向善(终极目标) | 强调技术发展应致力于增进人类福祉、促进社会公平、保障安全可控、维护伦理道德。需要从设计、应用到监管实现全链条的“向善”。 |
| 观察八:人才培养体系创新 | 领域内急需跨学科复合型人才。需通过高校课程改革、企业内训及产学研合作来弥补巨大的人才缺口。 |
| 观察九:政策扶持加速发展 | 中国从中央到地方(如北京、上海、深圳、重庆)出台了密集的扶持政策,从技术攻关、产业协同、应用场景开放等多方面加速产业发展。 |
| 观察十:激烈的国际竞争 | 竞争已超越商业范畴,延伸至国家战略层面(如美国科技与国防结合)。中国需强化自主创新、完善产业政策以应对技术封锁和贸易壁垒。 |
🚀 总结与展望
回顾: 具身智能在技术、应用和产业生态上已取得显著进展,但仍在核心技术、成本、数据、人才和伦理等方面面临挑战。展望: 未来,随着技术的持续迭代和应用场景的不断拓展,具身智能产业将进入高速发展期。为确保其健康发展,报告建议:
- 1.技术与应用: 加大核心技朧研发,鼓励在多场景的应用拓展。
- 2.治理与规范: 完善数据治理体系,加快伦理安全标准制定。
- 3.人才与生态: 创新人才培养模式,优化政策支持环境。
- 4.合作与向善: 在积极参与国际合作与竞争的同时,坚守“智能向善”的终极目标,确保技术发展服务于人类福祉。
中文版报告原文:
English Version
Ten Major Observations on Embodied Intelligence (November 2025) – Summary Report
📖 Document Overview
Report Title: Ten Major Observations on Embodied IntelligenceCore Theme: Insight into the Trends of Intelligent Development, Exploring the Path to Beneficial AIRelease Date: November 2025Key Summary: This report systematically examines the latest developments in Embodied AI across technological breakthroughs, industrial development, application scenarios, and governance systems. It highlights that, driven by advances in large models and multimodal technologies, Embodied Intelligence is becoming a significant new engine for economic growth. However, challenges remain in technological bottlenecks, data governance, ethics, safety, and talent shortage. The ultimate goal is to achieve « AI for Good. »
🔍 Detailed Analysis of the Ten Key Observations
Observation 1: Core Driving Technologies – Large Models and Multimodal Integration
Large model technology provides Embodied AI with a powerful « brain, » significantly enhancing semantic understanding, decision-making, and environmental adaptability.The integration of multimodal perception and interaction technologies (vision, hearing, touch) enables robots to perceive their environment more comprehensively and interact naturally.

Challenges: High computational resource demands, insufficient data quality and diversity, model interpretability and safety, hardware standardization issues.Solutions: Algorithm and hardware optimization, use of synthetic data (e.g., NVIDIA Isaac GR00T), research into explainable AI, promotion of hardware standardization.

Observation 2: Industrial Chain Bottlenecks – Key Nodes Await Breakthroughs
The report analyzes the complete industrial chain of Embodied AI.
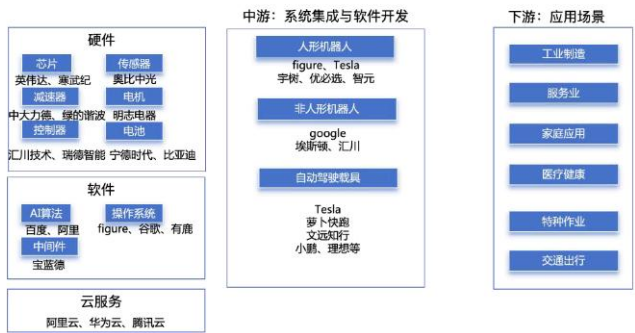
- ∙Upstream (Core Components/Algorithms): Bottlenecks persist in high-end AI chips (e.g., NVIDIA), sensors, servo motors, etc. Domestic substitution is accelerating.
- ∙Midstream (System Integration/Product Manufacturing): High difficulty in hardware-software integration. The supply chain for the « brain » (cognitive models) and « cerebellum » (motion control) models needs further improvement.
- ∙Downstream (Application Scenarios): Market demand feedback drives optimization and upgrading of the industrial chain.
Observation 3: Application Scenarios – Industrial Manufacturing as the Primary Breakthrough
Factory scenarios, with their clear tasks, controlled environments, and existing automation foundation, have become the first area for large-scale deployment of humanoid robots.
- ∙Industrial « Internship » Wave: Humanoid robots like Tesla’s Optimus, Figure’s Figure 02 in BMW factories, and Ubtech’s Walker S in China are performing tasks such as handling, assembly, and quality inspection in automotive plants.
- ∙Service and Special Operations: Service robots (e.g., 1X’s EVE) expand into security, logistics, and elderly care. Specialized robots are used in hazardous and complex environments like firefighting, mining, and deep-sea operations.

Expansion Obstacles: Insufficient technical capabilities in complex environments, high costs, need to improve market acceptance.
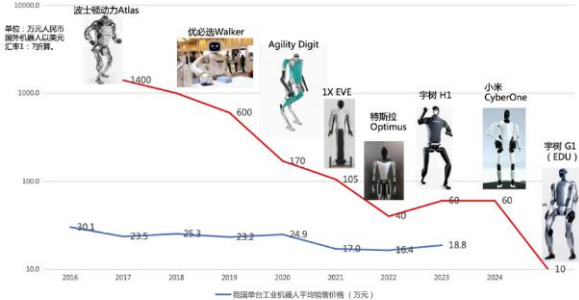
Observation 4: Market Competition – Increasingly Intense
- ∙Market Forecast: The global Embodied AI systems market is projected to grow from 3.5billionin2023to9.4 billion by 2030 (CAGR 15.2%).
- ∙International Giants’ Layout:
- ∙NVIDIA: Building a full-stack ecosystem (« Chip-Platform-Model-Simulation ») with products like Jetson chips, the GR00T model, and the Isaac Sim simulation platform.
- ∙Tesla: Replicating its automotive « mass manufacturing + AI chips + data闭环 » model for the Optimus humanoid robot, aiming to reduce costs below $18,000.
- ∙Others: Google (RT series models), OpenAI (investing in Figure AI), etc., are actively involved.
- ∙Domestic Enterprises: Startups and tech giants like Huawei, Xiaomi, Unitree Robotics, and Magic Atom are seeking breakthroughs in specific areas.

Observations 5-10: Foundations and Direction of Development
| Observation Area | Key Summary |
|---|---|
| Observation 5: Data Governance & Privacy Protection | Data is the « fuel » for Embodied AI. Challenges in data collection and annotation must be addressed. Data security and privacy are ensured through encryption, access control, and robust management systems. |
| Observation 6: Ethical & Safety Standards | Ethical issues in human-robot interaction and risks of robot malfunction must be prevented. Standards are being developed internationally (e.g., EU AI Act). Enterprises must integrate safety and ethics into design. |
| Observation 7: AI for Good (Ultimate Goal) | Technological development should enhance human well-being, promote social equity, ensure safety/controllability, and uphold ethics. A « for good » approach is needed throughout the entire chain from design to regulation. |
| Observation 8: Innovation in Talent Cultivation | There is a high demand for interdisciplinary talent. Addressing the significant talent gap requires university curriculum reform, corporate training, and industry-academia collaboration. |
| Observation 9: Policy Support Accelerates Development | China has introduced intensive support policies at national and local levels (e.g., Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Chongqing) to accelerate industry development through R&D support, industrial synergy, and open application scenarios. |
| Observation 10: Fierce International Competition | Competition extends beyond commerce to national strategy (e.g., US tech-defense integration). China needs to strengthen independent innovation and improve industrial policies to address technological blockades and trade barriers. |
🚀 Conclusion and Outlook
Retrospective: Significant progress has been made in the technology, applications, and industrial ecosystem of Embodied AI, but challenges remain in core technologies, cost, data, talent, and ethics.Outlook: As technology continues to evolve and application scenarios expand, the Embodied AI industry is poised for rapid growth. To ensure healthy development, the report recommends:
- 1.Technology & Application: Increase R&D in core technologies and encourage application across diverse scenarios.
- 2.Governance & Standards: Improve data governance systems and accelerate the establishment of ethical and safety standards.
- 3.Talent & Ecosystem: Innovate talent cultivation models and optimize the policy support environment.
- 4.Cooperation & Beneficial AI: While actively participating in international cooperation and competition, adhere to the ultimate goal of « AI for Good, » ensuring technological development serves human well-being.
No responses yet